- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Human Infestation with Dermanyssus gallinae (Acari: Dermanyssidae) in a Family Referred with Pruritus and Skin Lesions.
Read this article at
There is no author summary for this article yet. Authors can add summaries to their articles on ScienceOpen to make them more accessible to a non-specialist audience.
Abstract
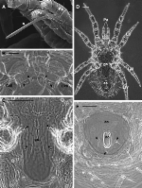
The poultry red mite, Dermanyssus gallinae is one of the most economically important ectoparasites in hens and some species of mammals worldwide. Cases of human infestation have been reported worldwide. In this study we report infestation in three members of a family referred with pruritus and allergic dermatitis rash. They have collected very small animals and carried them to the laboratory which later was confirmed as D. gallinae. They claimed that they had been bitten with this ectoparasite. This is the first case report of human infestation owing to D. gallinae from Iran.
Related collections
Most cited references21
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Pseudoscabies caused by Dermanyssus gallinae in Italian city dwellers: a new setting for an old dermatitis.
Gabriele Schino, M Lomuto, E Circella … (2008)
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Dermatitis in humans associated with the mites Pyemotes tritici, Dermanyssus gallinae, Ornithonyssus bacoti and Androlaelaps casalis in Israel.
Y Braverman, I Yeruham, Lee S. Rosen (2002)