- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Prevalence of Maxillary and Mandibular Frenal Attachment and Its Association with Age, Gender, and Oral Hygiene Status in Nepalese Population Seeking Dental Treatment
Read this article at
Abstract
Objective
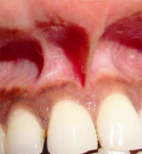
Frenum attachments are folds of mucous membrane that connect the lips to the alveolar mucosa and underlying periosteum. Aberrant positioning of the maxillary and mandibular labial frenum can lead to various clinical issues, including mucogingival problems and midline diastema. The objective of this study was to assess the prevalence of maxillary and mandibular frenal attachments and their association with age, gender, and oral hygiene status in the Nepalese population seeking dental treatment.
Materials and Methods
This descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted over a period of 6 months, from February 2023 to August 2023, among patients visiting the Department of Periodontology and Oral Implantology, aged 6 years and above, after obtaining official permission from the Institutional Review Committee (IRC-KUSMS Approval No. 8/23). The study collected data on morphological variations of frenal attachment and various periodontal parameters such as Oral Hygiene Index-Simplified (OHI-S), pocket depth, recession, and midline diastema in both arches. Descriptive statistics, including frequency and percentage, were used to analyze the data. The χ 2-test was employed to determine the correlation between gender and types of frenulum attachment, while analysis of variance was used to assess the association of frenal attachments with oral hygiene status.
Results
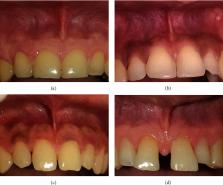
Among 380 patients, the prevalence of frenal attachment was as follows: gingival 248 (65.30%), mucosal 71 (18.70%), papillary 42 (11.10%), and papillary penetrating 19 (5.00%) in the maxilla, and mucosal 225 (59.20%) and gingival 155 (40.78%) in mandible. Among the different morphological variations of frenal attachments, normal frenum was the most common, accounting for 231 cases (60.80%), followed by frenum with a nodule, with 101 cases (26.60%).
Related collections
Most cited references40
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Significance of the labial frenum attachment in periodontal disease in man. Part I. Classification and epidemiology of the labial frenum attachment.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
An overview of frenal attachments
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found