- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Long non-coding RNA-X-inactive specific transcript inhibits cell viability, and induces apoptosis through the microRNA-30c-5p/Bcl2-like protein 11 signaling axis in human granulosa-like tumor cells
Read this article at
ABSTRACT
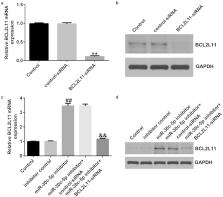
The role of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) is being actively explored in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Recent research has shown that long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) X–inactive Specific Transcript (XIST) is overexpressed in patients with PCOS and is associated with poor pregnancy outcomes. However, the precise function and mechanism of action of lncRNA XIST in PCOS are unknown. We aimed to determine whether lncRNA XIST contributes to PCOS by modulating ovarian granulosa cell physiology. We also investigated any potential molecular regulatory mechanisms. In this study, we discovered that the lncRNA XIST was significantly downregulated in human ovarian granulosa-like tumor (KGN) cells. Notably, overexpression of lncRNA XIST decreased miR-30c-5p expression in KGN cells, inhibited proliferation, and induced apoptosis in KGN cells. However, cotransfection with amiR-30c-5p mimic significantly reduced these effects. Additionally, we discovered that the miR-30c-5p mimic effectively inhibited Bcl2-like protein 11 (BCL2L11) expression, a critical apoptotic promoter, whereas silencing of miR-30c-5p increased BCL2L11 expression, inhibited KGN cell proliferation, and induced apoptosis. In contrast, cotransfection of BCL2L11 with siRNA significantly reversed these effects. In conclusion, this study established that lncRNA XIST plays a critical role in PCOS by modulating the miR-30c-5p/BCL2L11 signaling axis and regulating ovarian granulosa cell physiology.
Graphical Abstract
Related collections
Most cited references47
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
