- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Role of Intravenous Selexipag in Managing PAH and Bridging Gaps in Oral Treatment: A Narrative Review
Read this article at
Abstract
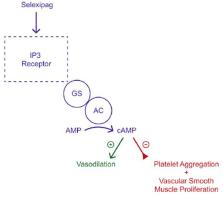
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a rare and potentially fatal condition characterized by progressive increases in blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs. Oral selexipag, approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2015 for the treatment of PAH, targets prostacyclin receptors on pulmonary arterial vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells to improve blood flow through the lungs and reduce pulmonary vascular resistance. Oral selexipag is effective, but may be discontinued due to factors like side effects, emergency conditions, or inability to take oral medication, potentially leading to severe adverse events, such as rebound pulmonary hypertension and right heart failure. To address treatment interruptions, intravenous (IV) selexipag was introduced as an alternative for patients who are temporarily unable to take oral medications. IV selexipag bypasses hepatic metabolism, requiring a 12.5% higher dose compared to the oral form to achieve similar therapeutic effects. It is administered via IV infusion twice daily over 80 minutes, typically for short-term use. However, caution is needed when prescribing selexipag to patients with hepatic or renal issues, and it is contraindicated with strong CYP2C8 inhibitors. A Phase III clinical trial confirmed that switching between oral and IV selexipag was safe, with comparable efficacy and tolerability, though it was limited by small sample size and short duration. Given the risks of treatment interruption and the complexity of managing PAH, this review provides essential insights into the practical use of IV selexipag as a bridging therapy. Furthermore, it calls for larger clinical trials to refine dosing strategies, explore long-term outcomes, and identify patient populations most likely to benefit from IV selexipag.
Plain Language Summary
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a rare and dangerous condition that causes high blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs, leading to right heart failure and potentially death. Selexipag is a medication used to treat patients with PAH by widening the blood vessels in the lungs. However, some patients may not be able to take oral selexipag as prescribed, which can worsen their condition. In 2021, an intravenous (IV) form of selexipag was approved as a temporary alternative for these patients. This review examines available literature to provide background and practical instruction for providers prescribing IV selexipag.
Unlike oral selexipag, which is processed by enzymes in the liver, the IV form bypasses liver metabolism and enters the bloodstream directly. As a result, the IV dose is typically 12.5% higher than the oral dose to achieve the same therapeutic effects. IV selexipag is administered twice daily through an infusion lasting about 80 minutes and is intended for temporary use. Healthcare providers should use caution when prescribing selexipag to patients with liver or kidney issues. Additionally, selexipag should not be used with medications that block CYP enzymes. A phase III clinical trial reports that common side effects of the IV form of selexipag include headaches and irritation at the injection site. While IV selexipag is considered safe and effective for short-term use, larger studies are needed to better understand how to manage transitions between oral and IV forms.
Related collections
Most cited references19
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Selexipag for the Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mechanisms of disease: pulmonary arterial hypertension
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.