- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Scaling up integrated prevention campaigns for global health: costs and cost-effectiveness in 70 countries
Read this article at
Abstract
Objective
This study estimated the health impact, cost and cost-effectiveness of an integrated prevention campaign (IPC) focused on diarrhoea, malaria and HIV in 70 countries ranked by per capita disability-adjusted life-year (DALY) burden for the three diseases.
Methods
We constructed a deterministic cost-effectiveness model portraying an IPC combining counselling and testing, cotrimoxazole prophylaxis, referral to treatment and condom distribution for HIV prevention; bed nets for malaria prevention; and provision of household water filters for diarrhoea prevention. We developed a mix of empirical and modelled cost and health impact estimates applied to all 70 countries. One-way, multiway and scenario sensitivity analyses were conducted to document the strength of our findings. We used a healthcare payer's perspective, discounted costs and DALYs at 3% per year and denominated cost in 2012 US dollars.
Primary and secondary outcomes
The primary outcome was cost-effectiveness expressed as net cost per DALY averted. Other outcomes included cost of the IPC; net IPC costs adjusted for averted and additional medical costs and DALYs averted.
Results
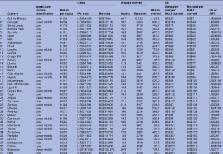
Implementation of the IPC in the 10 most cost-effective countries at 15% population coverage would cost US$583 million over 3 years (adjusted costs of US$398 million), averting 8.0 million DALYs. Extending IPC programmes to all 70 of the identified high-burden countries at 15% coverage would cost an adjusted US$51.3 billion and avert 78.7 million DALYs. Incremental cost-effectiveness ranged from US$49 per DALY averted for the 10 countries with the most favourable cost-effectiveness to US$119, US$181, US$335, US$1692 and US$8340 per DALY averted as each successive group of 10 countries is added ordered by decreasing cost-effectiveness.
Related collections
Most cited references58
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Insecticide-treated bed nets and curtains for preventing malaria.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found