- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Hepatoprotective Effect of Cranberry Nutraceutical Extract in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Model in Rats: Impact on Insulin Resistance and Nrf-2 Expression
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a pathological accumulation of triglycerides (TGs) in the hepatocyte in the absence of alcohol intake. Untreated NAFLD is expected to progress into liver fibrosis. Cranberry is rich in polyphenols with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities.
Hypothesis
The present study was performed to evaluate our hypothesis of the possible anti-fibrotic effect of cranberry nutraceuticals in a high fat cholesterol diet induced (HFCD)-NAFLD in rats, focusing on improving insulin sensitivity and modulating the expression of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor-2 (Nrf2) (a transcription factor responsible for regulating cellular redox balance).
Method
Male albino wistar rats (12 weeks) received HFCD and/or cranberry (50 and 100 mg/kg/day, three times/week) orally for 8 consecutive weeks.
Results
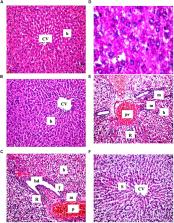
In comparison to the HFCD group, cranberry treated groups (50 and 100 mg/kg) showed marked hepatoprotection, where it significantly decreased liver enzymes (alanine transaminases by 49 and 64% and aspartate transaminases by 45 and 64%; respectively), TGs, and ameliorated the histopathological alterations (such as inflammatory cells infiltration and ballooning degeneration) induced by HFCD. Cranberry also alleviated oxidative stress (malondialdehyde, glutathione, catalase and superoxide dismutase) and inflammation (tumor necrosis factor- alpha, interleukine-6 and nuclear factor kappa-b) and significantly reduced the HOMA-IR and TyG index. On the other hand, cranberry treated groups (50 and 100 mg/kg) showed a marked increase in the expression of adiponectin, by 8 and 13-fold, insulin receptor substrate-2 by 21 and 79%, and Nrf2 by 13 and 61%, respectively. Notably, cranberry significantly reduced the fibrotic markers, TGF–β and α-SMA expression and collagen deposition.
Conclusion
The present study showed that cranberry significantly attenuated NAFLD, in a dose dependent manner, which could be partially recognized by its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory activities, and its ability to improve insulin sensitivity. Notably, our study proves for the first time that the anti-fibrotic activity of cranberry is promising.
Related collections
Most cited references55
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Review: The role of insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found