- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Sensitive isothermal detection of nucleic-acid sequence by primer generation–rolling circle amplification
Read this article at
Abstract
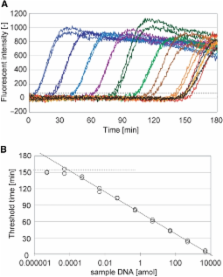
A simple isothermal nucleic-acid amplification reaction, primer generation–rolling circle amplification (PG–RCA), was developed to detect specific nucleic-acid sequences of sample DNA. This amplification method is achievable at a constant temperature (e.g. 60°C) simply by mixing circular single-stranded DNA probe, DNA polymerase and nicking enzyme. Unlike conventional nucleic-acid amplification reactions such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), this reaction does not require exogenous primers, which often cause primer dimerization or non-specific amplification. Instead, ‘primers’ are generated and accumulated during the reaction. The circular probe carries only two sequences: (i) a hybridization sequence to the sample DNA and (ii) a recognition sequence of the nicking enzyme. In PG–RCA, the circular probe first hybridizes with the sample DNA, and then a cascade reaction of linear rolling circle amplification and nicking reactions takes place. In contrast with conventional linear rolling circle amplification, the signal amplification is in an exponential mode since many copies of ‘primers’ are successively produced by multiple nicking reactions. Under the optimized condition, we obtained a remarkable sensitivity of 84.5 ymol (50.7 molecules) of synthetic sample DNA and 0.163 pg (∼60 molecules) of genomic DNA from Listeria monocytogenes, indicating strong applicability of PG–RCA to various molecular diagnostic assays.
Related collections
Most cited references19
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mutation detection and single-molecule counting using isothermal rolling-circle amplification.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found