- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Craniofacial morphology in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: cephalometric evaluation
Abstract
Introduction
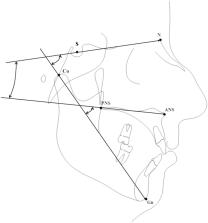
Obstructive sleep apnea is characterized by a reduced airflow through the upper airways during sleep. Two forms of obstructive sleep apnea are described: the central form and the obstructive form. The obstructive form is related to many factors, such as the craniofacial morphology.
Objective
To evaluate the correlation between the morphology of the cranial base, of the mandible and the maxilla, and obstructive sleep apnea severity.
Methods
Eighty-four patients, mean age of 50.4 years old; 73 males and 11 females with obstructive sleep apnea were enrolled in the present study. Patients with high body mass index and comorbidities were excluded. Lateral cephalograms and polysomnography were collected for each patient to evaluate the correlation between craniofacial morphology and obstructive sleep apnea severity. A Spearman’s rho correlation test between cephalometric measurements and obstructive sleep apnea indexes was computed. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
Results
Patients with a severe obstructive sleep apnea presented a reduction of sagittal growth of both effective mandibular length and cranio-basal length. The mandibular length was the only variable with a statistical correlation with apnea-hypopnea index. Vertical dimension showed a weak correlation with the severity of obstructive sleep apnea. No correlation with maxillary sagittal dimension was shown.
Related collections
Most cited references43
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnostic Testing for Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found