- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The genome sequence and demographic history of Przewalskia tangutica (Solanaceae), an endangered alpine plant on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau
Read this article at
Abstract
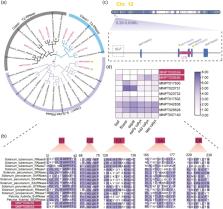
To adapt to high-altitude habitats, many alpine plants develop self-compatible breeding systems from outcrossing. The genetic bases for this shift and the resulting demographic consequences remain largely unexplored. Here, we present a high-quality, chromosome-level genome assembly of the monotypic and endangered alpine perennial Przewalskia tangutica (Solanaceae) occurring on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau (QTP). Our assembled genome is approximately 3 Gb, with a contig N50 size of 17 Mb, and we identified one lineage-specific whole-genome duplication. We found that the gametophytic self-incompatibility (GSI) syntenic locus to the other obligate outcrossing Solanaceae species was broken by the inserted the long terminal repeats, and changes in the flower-specific expression of the homologous genes, and the linked GSI genes in this species. Such changes may have led to its self-compatibility. We identified three deeply diverged lineages in the central distribution of this species, and the gene flow between them was weak but continuous. All three lineages diverged and decreased their population sizes since the largest glaciations occurred in the QTP approximately 720–500 thousand years ago. In addition, we identified one obvious hybrid population between two lineages, suggesting that genetic exchanges between and within lineages still occur. Our results provide insights into evolutionary adaptation through facultative self-pollination and demographic consequences of this alpine rare species in arid habitats.
Related collections
Most cited references96

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found