- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Different Subsets of T Cells, Memory, Effector Functions, and CAR-T Immunotherapy
Read this article at
Abstract
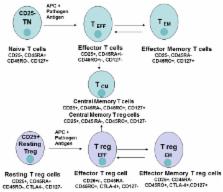
This review is focused on different subsets of T cells: CD4 and CD8, memory and effector functions, and their role in CAR-T therapy––a cellular adoptive immunotherapy with T cells expressing chimeric antigen receptor. The CAR-T cells recognize tumor antigens and induce cytotoxic activities against tumor cells. Recently, differences in T cell functions and the role of memory and effector T cells were shown to be important in CAR-T cell immunotherapy. The CD4 + subsets (Th1, Th2, Th9, Th17, Th22, Treg, and Tfh) and CD8 + memory and effector subsets differ in extra-cellular (CD25, CD45RO, CD45RA, CCR-7, L-Selectin [CD62L], etc.); intracellular markers (FOXP3); epigenetic and genetic programs; and metabolic pathways (catabolic or anabolic); and these differences can be modulated to improve CAR-T therapy. In addition, CD4 + Treg cells suppress the efficacy of CAR-T cell therapy, and different approaches to overcome this suppression are discussed in this review. Thus, next-generation CAR-T immunotherapy can be improved, based on our knowledge of T cell subsets functions, differentiation, proliferation, and signaling pathways to generate more active CAR-T cells against tumors.
Related collections
Most cited references27
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Fueling immunity: insights into metabolism and lymphocyte function.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found