- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Impact of M2BPGi on the Hepatocarcinogenesis after the Combination Therapy with Daclatasvir and Asunaprevir for Hepatitis C
Read this article at
Abstract
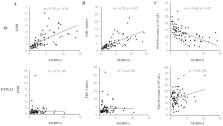
The clinical significance of mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer (M2BPGi) levels based on virological responses due to antiviral therapy has not been fully evaluated. We compared the change before and 24 weeks after the therapy with daclatasvir and asunaprevir (DCV+ASV) of M2BPGi levels with those of other fibrosis markers in 73 chronic hepatitis C cases. Moreover, we examined the association between M2BPGi levels and hepatocarcinogenesis in sustained virological response (SVR) and non-SVR cases. M2BPGi levels were significantly improved at post-treatment week 24 (PTW24) in SVR but not non-SVR cases, whereas the changes of other fibrosis markers showed the same tendency in both SVR and non-SVR cases. M2BPGi levels were well correlated with other fibrosis markers at baseline but not PTW24. The incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) was significantly associated with M2BPGi levels at PTW24. The achievement of SVR significantly affected the improvement of M2BPGi levels that best reflected the effect of direct-acting antivirals among the fibrosis markers. Furthermore, M2BPGi levels at PTW24 were also associated with the incidence of HCC in only SVR cases. However, the rapid decrease of M2BPGi levels might reflect the amelioration of liver inflammation rather than the improvement of liver fibrosis, which should be further elucidated.
Related collections
Most cited references31

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR' for medical statistics
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found