- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Interleukin-8 promotes cell migration via CXCR1 and CXCR2 in liver cancer
Read this article at
Abstract
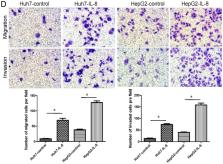
Liver cancer (LC), which is one of the most common types of cancer worldwide, is notorious for its high morbidity and mortality rates. Interleukin-8 (IL-8), an important member of the CXC chemokine family that was originally classified as a potent neutrophil chemoattractant, has been shown to serve an important role in inflammation, tumor growth, invasion and metastasis through interactions with its receptors. However, the expression and functional roles of IL-8 and its receptors, CXC chemokine receptor (CXCR) 1 and CXCR2 in the progression of liver cancer remain to be fully elucidated. In the present study, it was shown that the mRNA levels of IL-8, CXCR1 and CXCR2 were increased in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with liver cancer compared with those from patients with cirrhosis or normal controls (P<0.05). Higher levels of CXCR1, CXCR2 and IL-8 were associated with advanced tumor stage and increased risk of lymph node or distant metastasis. Immunohistochemistry showed that the IL-8, CXCR1 and CXCR2 proteins were expressed in the cytoplasm of hepatoma cells at higher intensities than those of normal controls (P<0.05). The semi-quantitative analysis revealed that the relative mean density of hepatic IL-8, CXCR1 and CXCR2 staining in liver cancer was significantly increased compared with that in normal liver tissues (P<0.05). The analysis revealed that the mRNA expression of IL-8 was positively associated with that of CXCR1 (r=0.618; P<0.05) and CXCR2 (r=0.569; P<0.05). The mRNA levels of CXCR1 and CXCR2 gradually increased with elevated expression of IL-8 in liver cancer. Experiments were performed using human Huh-7 and HepG2 cell lines, incubating cells with IL-8 and conducting in vitro migration and invasion assays. The results showed that the wound healing activity and migration of Huh-7 and HepG2 cells were increased by IL-8. Pretreatment of the cells with anti-CXCR1 or anti-CXCR2 (5 µM) for 30 min markedly inhibited IL-8-directed cell migration. Taken together, these results indicated that IL-8 promotes liver cancer cell migration via CXCR1 and CXCR2 and that targeting the CXCR1/2 may be a potential strategy for liver cancer treatment.
Related collections
Most cited references20
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The tumour-induced systemic environment as a critical regulator of cancer progression and metastasis.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Role of the CXCL8-CXCR1/2 Axis in Cancer and Inflammatory Diseases

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found