- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Content validity of SarQoL, a quality of life questionnaire specific to sarcopenia
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
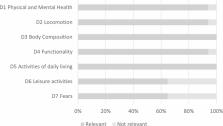
The Sarcopenia & Quality of Life (SarQoL) questionnaire is a patient-reported outcome measure designed for assessing health-related quality of life in individuals with sarcopenia. Despite its wide acceptance in the scientific literature, its content validity has only been partially demonstrated so far.
Methods
Following COSMIN methodology, semi-structured interviews were conducted with 17 Belgian older adults who met the EWGSOP2 criteria for the diagnosis of sarcopenia and 11 experts in sarcopenia, with clinical or research background. Comprehensiveness, relevance and comprehensibility of SarQoL content were assessed through individual transcripts and were qualitatively analyzed thematically according to the seven dimensions of SarQoL.
Results
The majority of the concepts elicited during the semi-structured interviews fitted within existing SarQoL dimensions. Importantly, the different domains of SarQoL were consensually considered as relevant by patients and experts. Some new emergent concepts were identified by the participants. While many of them could be considered as enrichments of existing dimensions or sub-concepts, other new concepts (i.e. self-fulfilment, acceptance of the reduced condition, adaptation/use of strategies, depression) may highlight two potential dimensions not covered by SarQoL, i.e. patient empowerment and depression. Cognitive interviews also highlighted that SarQoL items and instructions were clear and comprehensible.
Conclusions
SarQoL, in its current form, demonstrates good evidence of content validity for assessing health-related quality of life in patients with sarcopenia. We do not recommend adding new items or dimensions to SarQoL. Instead, for researchers or clinicians who aim to specifically address self-empowerment or depression of sarcopenic populations, we suggest completing the assessment of quality of life by concurrently using additional validated scales of patient empowerment or depression.
Related collections
Most cited references32

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The COSMIN study reached international consensus on taxonomy, terminology, and definitions of measurement properties for health-related patient-reported outcomes.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found