- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Urinary Angiopoietin-2 Is Associated with Albuminuria in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Read this article at
Abstract
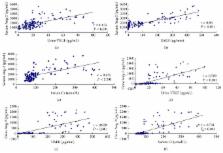
Aims. To evaluate the levels of angiopoietin-1 (Ang-1), Ang-2, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in serum and urine, and their association with albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Methods. In 113 type 2 diabetic patients with normoalbuminuria, microalbuminuria, and macroalbuminuria and 30 healthy controls, the levels of Ang-1, Ang-2, and VEGF in serum and urine were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Results. Urinary and serum levels of Ang-2 were significantly higher in diabetic patients with normoalbuminuria than in healthy controls. Increased urinary Ang-2 level was positively associated with the degree of albuminuria. Urinary Ang-1 levels were significantly higher in normoalbuminuria patients and lower in macroalbuminuria patients than in controls. The levels of urinary VEGF increased in the albuminuria subgroup, though serum levels of Ang-1 and VEGF did not change. Urinary Ang-2 levels were correlated positively with albuminuria and negatively with glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Stepwise multiple regression analysis identified albuminuria ( P < 0.001) and GFR ( P = 0.001) as significant predictors of urinary Ang-2. Conclusions. Our data suggest that urinary Ang-2 is stepwise increased with renal damage in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and is associated with albuminuria.
Related collections
Most cited references43
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines and Clinical Practice Recommendations for Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Angiopoietin-2, a natural antagonist for Tie2 that disrupts in vivo angiogenesis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found