- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Effects of site-directed mutagenesis of mglA on motility and swarming of Myxococcus xanthus
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
The mglA gene from the bacterium Myxococcus xanthus encodes a 22kDa protein related to the Ras superfamily of monomeric GTPases. MglA is required for the normal function of A-motility ( adventurous), S-motility ( social), fruiting body morphogenesis, and sporulation. MglA and its homologs differ from all eukaryotic and other prokaryotic GTPases because they have a threonine (Thr78) in place of the highly conserved aspartate residue of the consensus PM3 ( phosphate- magnesium binding) region. To identify residues critical for MglA function or potential protein interactions, and explore the function of Thr78, the phenotypes of 18 mglA mutants were characterized.
Results
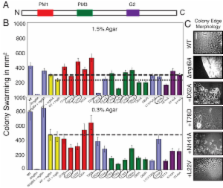
Nine mutants, with mutations predicted to alter residues that bind the guanine base or coordinate magnesium, did not produce detectable MglA. As expected, these mutants were mot - dev - because MglA is essential for these processes. Of the remaining nine mutants, seven showed a wild-type distribution pattern for MglA but fell into two categories with regard to function. Five of the seven mutants exhibited mild phenotypes, but two mutants, T78D and P80A, abolished motility and development. The localization pattern of MglA was abolished in two mutants that were mot - spo - and dev -. These two mutants were predicted to alter surface residues at Asp52 and Thr54, which suggests that these residues are critical for proper localization and may define a protein interaction site. Improving the consensus match with Ras at Thr78 abolished function of MglA. Only the conservative serine substitution was tolerated at this position. Merodiploid constructs revealed that a subset of alleles, including mglAD52A, were dominant and also illustrated that changing the balance of MglA and its co-transcribed partner, MglB, affects A-motility.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that GTP binding is critical for stability of MglA because MglA does not accumulate in mutants that cannot bind GTP. The threonine in PM3 of MglA proteins represents a novel modification of the highly conserved GTPase consensus at this position. The requirement for a hydroxyl group at this position may indicate that MglA is subject to modification under certain conditions. Proper localization of MglA is critical for both motility and development and likely involves protein interactions mediated by residues Asp52 and Thr54.
Related collections
Most cited references47
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Small GTP-binding proteins.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Geobacter metallireducens accesses insoluble Fe(III) oxide by chemotaxis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found