- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A novel prognostic N 7-methylguanosine-related long non-coding RNA signature in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Read this article at
Abstract
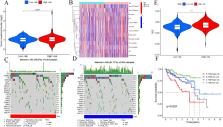
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is regulated by methylation modifications and long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs). However, knowledge of N 7-methylguanosine (m 7G)-related lncRNAs that predict ccRCC prognosis remains insufficient. A prognostic multi-lncRNA signature was created using LASSO regression to examine the differential expression of m7G-related lncRNAs in ccRCC. Furthermore, we performed Kaplan–Meier analysis and area under the curve (AUC) analysis for diagnosis. In all, a model based on five lncRNAs was developed. Principal component analysis (PCA) indicated that the risk model precisely separated the patients into different groups. The IC 50 value for drug sensitivity divided patients into two risk groups. High-risk group of patients was more susceptible to A.443654, A.770041, ABT.888, AMG.706, and AZ628. Moreover, a lower tumor mutation burden combined with low-risk scores was associated with a better prognosis of ccRCC. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) exhibited that the expression levels of LINC01507, AC093278.2 were very high in all five ccRCC cell lines, AC084876.1 was upregulated in all ccRCC cell lines except 786-O, and the levels of AL118508.1 and DUXAP8 were upregulated in the Caki-1 cell line. This risk model may be promising for the clinical prediction of prognosis and immunotherapeutic responses in patients with ccRCC.
Related collections
Most cited references42
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found