- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Impact of Hypoxia-Induced miR-210 on Pancreatic Cancer
Read this article at
Abstract
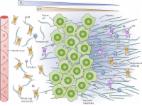
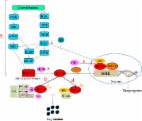
Pancreatic cancer (PC) poses significant clinical challenges, with late-stage diagnosis and limited therapeutic options contributing to its dismal prognosis. A hallmark feature of PC is the presence of a profoundly hypoxic tumour microenvironment, resulting from various factors such as fibrotic stroma, rapid tumour cell proliferation, and poor vascularization. Hypoxia plays a crucial role in promoting aggressive cancer behaviour, therapeutic resistance, and immunosuppression. Previous studies have explored the molecular mechanisms behind hypoxia-induced changes in PC, focusing on the role of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs). Among the myriad of molecules affected by hypoxia, microRNA-210 (miR-210) emerges as a central player. It is highly responsive to hypoxia and regulated by HIF-dependent and HIF-independent pathways. miR-210 influences critical cellular processes, including angiogenesis, metastasis, and apoptosis, all of which contribute to PC progression and resistance to treatment. Understanding these pathways provides insights into potential therapeutic targets. Furthermore, investigating the role of miR-210 and its regulation in hypoxia sheds light on the potential development of early diagnostic strategies, which are urgently needed to improve outcomes for PC patients. This review delves into the complexities of PC and introduces the roles of hypoxia and miR-210 in the progression of PC.
Related collections
Most cited references111
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
HIF-1α pathway: role, regulation and intervention for cancer therapy
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension.