- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Cultivable oral bacteriota dysbiosis in mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients
Read this article at
Abstract
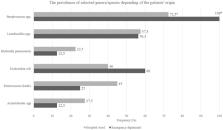
Potential interactions between the SARS-CoV-2 virus and the human oral microbiota are currently investigated widely. Patients with COVID-19 requiring mechanical ventilation in an intensive care unit (ICU) setting are at high risk of developing severe complications, including ventilator-associated pneumonia, thus making oral health management important. The aim of this study was to evaluate the oral health status and assess the dysbiosis of cultivable oral bacteriota in COVID-19 patients hospitalized in an ICU with acute respiratory distress within 36 h following intubation. In this prospective cohort study, we recruited 56 adult COVID-19 patients that qualified for mechanical ventilation in the Temporary ICU for COVID-19 Patients of the University Hospital in Krakow. On admission to the ICU, oral health of patients was assessed using the modified Beck Oral Assessment Score (BOAS). Four oral habitats were sampled, namely the buccal mucosa, tongue, buccal dental surface and gingival pocket. Microorganisms were identified by MALDI/TOF mass spectrometry. The mean age of the study population was 66.5 ± 12.7 years, there were 24 (42.9%) females. All patients included in this study were intubated and ventilated in the ICU, with a corresponding high mortality rate (76.8%). On admission to ICU, 76.8% subjects scored 11–20 on the BOAS scale (median 12 [IQR 10–14]), indicating moderate or severe dysfunction of oral health. Potentially pathogenic bacteria were identified in the oral microbiota samples, including Acinetobacter baumannii, Enterococcus faecalis, Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in 23.2%, 39.3%, 17.9%, and 19.6% of patients, respectively. Lactobacillus spp. were present in 57.1% subjects. The mean CFU counts of all bacteria strains in dental brushes were 9.3E+5 (1.4E+6) and in gingival pockets 7.6E+5 (1.4E+6). The highest CFU counts were observed for Enterococcus spp. and, Lactobacillus spp., although these did not differ significantly from CFU counts of Streptococcus spp. and Staphylococcus spp. In this report we comprehensively characterized the oral health condition and cultivable oral bacteriota in COVID-19 patients hospitalized in an ICU with acute respiratory distress within 36 h following intubation. The oral bacteriota showed significant qualitative and quantitative dysbiosis. Hospitalization in an ICU and mechanical ventilation are important factors leading to oral dysbiosis in SARS-CoV-2 patients.
Related collections
Most cited references47
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found