- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Feasibility of split-course stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for oligometastases
Read this article at
Abstract
Split-course stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) appeared to achieve favorable toxicity profiles and local control outcomes comparable with those of continuous SABR in the patients with oligometastases.
Abstract
Background
There is growing interest in the use of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) for oligometastases. However, extreme caution should be exercised in treating tumors closely located to organs at risk (OARs) with SABR. To reduce complications, we have applied split-course SABR to oligometastases closely located to OARs or to those being retreated with radiotherapy.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the records of patients with oligometastases who were treated with planned split-course SABR between January 2012 and December 2016.
Results
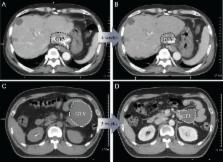
A total of 23 patients with 29 oligometastatic lesions were enrolled. The primary diagnoses were bone and soft tissue cancers in 13 lesions, liver cancers in 12 lesions, and colorectal cancers in four lesions. The median tumor volume was 78 cm 3 (range, 4–1781 cm 3). The lesions were treated with 1–3 fractions in the first stage of SABR (first SABR), and one or two fractions in the second stage of SABR (second SABR). The time interval between the two stages was about 4 weeks. A partial response was noted in 16 lesions (55%) after the first SABR, and practical reductions in the doses to OARs were observed in the second SABR compared with the first SABR. The 1-, 2- and 3-year local control rates were 92%, 65% and 43%, respectively. No Grade 4 or 5 toxicities were observed during or after treatment.
Related collections
Most cited references33
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Oligometastases revisited.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found