- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
LncRNA HOTAIR influences cell growth, migration, invasion, and apoptosis via the miR‐20a‐5p/ HMGA2 axis in breast cancer
Read this article at
Abstract
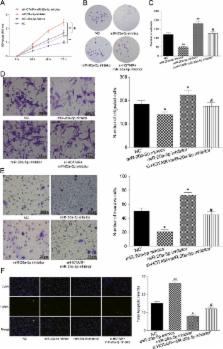
To study the regulatory effect of lnc RNA HOTAIR/miR‐20a‐5p/ HMGA2 axis on breast cancer ( BC) cell growth, cell mobility, invasiveness, and apoptosis. The microarray data of lnc RNAs and mRNAs with differential expression in BC tissues were analyzed in the Cancer Genome Atlas ( TCGA) database. Lnc RNA HOX transcript antisense RNA (lnc RNA HOTAIR) expression in BC was assessed by qRT‐ PCR. Cell viability was confirmed using MTT and colony formation assay. Cell apoptosis was analyzed by TdT‐mediated dUTP nick‐end labeling ( TUNEL) assay. Cell mobility and invasiveness were testified by transwell assay. RNA pull‐down and dual luciferase assay were used for analysis of the correlation between lnc RNA HOTAIR and miR‐20a‐5p, as well as relationship of miR‐20a‐5p with high mobility group AT‐hook 2 ( HMGA2 ). Tumor xenograft study was applied to confirm the correlation of lnc RNA HOTAIR/miR‐20a‐5p/ HMGA2 axis on BC development in vivo. The expression levels of the lnc RNA HOTAIR were upregulated in BC tissues and cells. Knockdown lnc RNA HOTAIR inhibited cell propagation and metastasis and facilitated cell apoptosis. MiR‐20a‐5p was a target of lnc RNA HOTAIR and had a negative correlation with lnc RNA HOTAIR. MiR‐20a‐5p overexpression in BC suppressed cell growth, mobility, and invasiveness and facilitated apoptosis. HMGA2 was a target of miR‐20a‐5p, which significantly induced carcinogenesis of BC. BC cells progression was mediated by lnc RNA HOTAIR via affecting miR‐20a‐5p/ HMGA2 in vivo. Lnc RNA HOTAIR affected cell growth, metastasis, and apoptosis via the miR‐20a‐5p/ HMGA2 axis in breast cancer.
Related collections
Most cited references29
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Roles of HMGA proteins in cancer.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Upregulation of miR-196a and HOTAIR drive malignant character in gastrointestinal stromal tumors.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found