- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Unfavorable social determinants of health and risk of mortality in adults with diabetes: findings from the National Health Interview Survey
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction
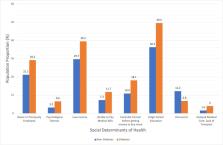
Understanding the role of social determinants of health as predictors of mortality in adults with diabetes may help improve health outcomes in this high-risk population. Using population-based, nationally representative data, this study investigated the cumulative effect of unfavorable social determinants on all-cause mortality in adults with diabetes.
Research design and methods
We used data from the 2013–2018 National Health Interview Survey, linked to the National Death Index through 2019, for mortality ascertainment. A total of 47 individual social determinants of health were used to categorize participants in quartiles denoting increasing levels of social disadvantage. Poisson regression was used to report age-adjusted mortality rates across increasing social burden. Multivariable Cox proportional hazards models were used to assess the association between cumulative social disadvantage and all-cause mortality in adults with diabetes, adjusting for traditional risk factors.
Results
The final sample comprised 182 445 adults, of whom 20 079 had diabetes. In the diabetes population, mortality rate increased from 1052.7 per 100 000 person-years in the first quartile (Q1) to 2073.1 in the fourth quartile (Q4). In multivariable models, individuals in Q4 experienced up to twofold higher mortality risk relative to those in Q1. This effect was observed similarly across gender and racial/ethnic subgroups, although with a relatively stronger association for non-Hispanic white participants compared with non-Hispanic black and Hispanic subpopulations.
Conclusions
Cumulative social disadvantage in individuals with diabetes is associated with over twofold higher risk of mortality, independent of established risk factors. Our findings call for action to screen for unfavorable social determinants and design novel interventions to mitigate the risk of mortality in this high-risk population.
Related collections
Most cited references29
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Obesity Phenotypes, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Social Determinants of Health and Diabetes: A Scientific Review

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found