- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Anticonvulsant and Antioxidant Effects of Musa sapientum Stem Extract on Acute and Chronic Experimental Models of Epilepsy

Read this article at
Abstract
Background:
Musa sapientum (banana) plant extract has been shown to possess antioxidant activity in previous studies. Neuronal injury resulting from oxidative stress is an important factor involved in pathogenesis of epilepsy.
Objective:
The present study aimed to evaluate the anticonvulsant activity of M. sapientum stem extract (MSSE) in acute and chronic experimental models in mice and its effects on various markers of oxidative stress in the brain of pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-kindled animals.
Material and Methods:
Maximal electroshock seizures (MES) and PTZ-induced convulsion models were used for acute studies. For the chronic study, the effect of MSSE on the development of kindling was studied. For the evaluation of the effects of MSSE on oxidative stress in brain, malondialdehyde (MDA) and reduced glutathione (GSH) levels were estimated in the brains of the kindled animals.
Results:
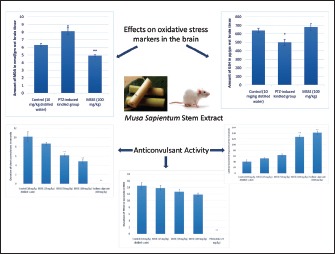
MSSE significantly increased the latency to onset of myoclonic jerks and the duration of clonic convulsions following PTZ administration. The MSSE pretreated group showed significantly reduced mean seizure score on PTZ-induced kindling. There was a significant increase in the brain MDA levels and decrease in GSH levels in response to PTZ-induced kindling. On MSSE pretreatment, there was a significant decrease in the MDA levels in the brains, though the increase in the GSH levels was not significant.
Conclusion:
The results from this study suggest the presence of significant anticonvulsant activity in MSSE, in both acute and chronic PTZ-induced seizure models, which could be due to its antioxidant activity, as is reflected by the change in oxidative stress markers in brain.
SUMMARY
-
Evaluation of the anticonvulsant activity of Musa sapientum and its effects on various markers of oxidative stress in the brain has not been done previously to the best of our knowledge
-
M. sapientum stem extract (MSSE) significantly increased the latency to onset of myoclonic jerks and the duration of clonic convulsions in the experimental models
-
The MSSE pretreated group showed significantly reduced mean seizure score on pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-induced kindling
-
There was significant increase in the brain malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and decrease in glutathione (GSH) levels in response to PTZ-induced kindling
-
On MSSE pretreatment, there was a significant decrease in the MDA levels in the brain, though the increase in the GSH levels was not significant.
Abbreviations Used: MSSE: Musa sapientum stem extract, PTZ: Pentylenetetrazole, MES: Maximal electroshock seizures, MDA: Malondialdehyde, GSH: Glutathione, SOD: Superoxide dismutase, THLE: Tonic hindlimb extension
Related collections
Most cited references37

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Neuroprotective potential of phytochemicals
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress: cause and consequence of epileptic seizures.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found