- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
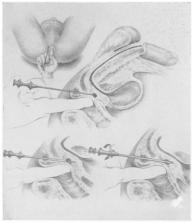
Hundred years of transperineal prostate biopsy
Read this article at
Abstract
The earliest recorded efforts to biopsy prostate, in the early 20th century, were made through transperineal (TP) approach, with open perineal prostate biopsy (PBx) being considered the gold standard for prostate cancer (PCa) diagnosis in that era. Later, to minimize morbidity and increase diagnostic accuracy, several technical modifications and transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) assistance were incorporated. However, in the 1980s, the transrectal (TR) approach became the predominant PBx method following the introduction of TRUS-TR PBx with sextant sampling, providing a convenient and efficacious method for prostate sampling. With modernization of PCa diagnosis, a recent resurgence of the TP PBx has been observed, driven primarily by TR drawbacks of infectious complications and sampling limitations. TP PBx is rapidly emerging as the new PBx standard, being officially recommended as the initial approach for biopsy in Europe and is increasingly being conducted and studied in the United States. The modern era of TP PBx is based on the improvements in local anesthesia techniques, TP access systems, and robotic assistance. These modifications and advancements have improved the ease of use, patient comfort, and diagnostic outcomes with TP PBx. Herein, we present a history of the evolution of TP PBx spanning over 100 years and explore the basis of the technique that merits future utilization.
Related collections
Most cited references91
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. Part II—2020 Update: Treatment of Relapsing and Metastatic Prostate Cancer
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found