- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Altered hippocampus and amygdala subregion connectome hierarchy in major depressive disorder
Read this article at
Abstract
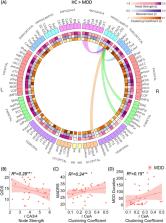
The hippocampus and amygdala limbic structures are critical to the etiology of major depressive disorder (MDD). However, there are no high-resolution characterizations of the role of their subregions in the whole brain network (connectome). Connectomic examination of these subregions can uncover disorder-related patterns that are otherwise missed when treated as single structures. 38 MDD patients and 40 healthy controls (HC) underwent anatomical and diffusion imaging using 7-Tesla MRI. Whole-brain segmentation was performed along with hippocampus and amygdala subregion segmentation, each representing a node in the connectome. Graph theory analysis was applied to examine the importance of the limbic subregions within the brain network using centrality features measured by node strength (sum of weights of the node’s connections), Betweenness (number of shortest paths that traverse the node), and clustering coefficient (how connected the node’s neighbors are to one another and forming a cluster). Compared to HC, MDD patients showed decreased node strength of the right hippocampus cornu ammonis (CA) 3/4, indicating decreased connectivity to the rest of the brain, and decreased clustering coefficient of the right dentate gyrus, implying it is less embedded in a cluster. Additionally, within the MDD group, the greater the embedding of the right amygdala central nucleus (CeA) in a cluster, the greater the severity of depressive symptoms. The altered role of these limbic subregions in the whole-brain connectome is related to diagnosis and depression severity, contributing to our understanding of the limbic system involvement in MDD and may elucidate the underlying mechanisms of depression.
Related collections
Most cited references76
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found