- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Colorful graphene-based wearable e-textiles prepared by co-dyeing cotton fabrics with natural dyes and reduced graphene oxide
Read this article at
Abstract
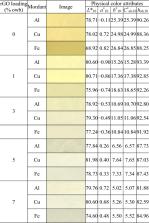
In addition to the functionality of electronic textiles (e-textiles), their aesthetic properties should be considered to expand their marketability. In this study, premordanted cotton fabrics were co-dyed with reduced graphene oxide (rGO) and natural dyes to develop ecofriendly and colorful graphene-based wearable e-textiles. The color attributes of the textiles were analyzed in terms of the dyeing conditions, namely, rGO loading, mordant type, and natural dye type. The lightness of the dyed samples increased in the order of cochineal < gardenia blue < rhubarb. Regardless of the natural dye and rGO loading, the lightness of the fabrics mordanted with Fe was lower than that with Al and Cu. Moreover, the rhubarb- and gardenia blue-dyed fabrics exhibited broad chroma and hue dispersions, indicating the strong impact of the dyeing conditions. With increasing rGO loading, the chroma of the rhubarb-dyed fabrics substantially decreased, resulting in decreased color saturation. The initial greenish-blue color of the gardenia blue-dyed fabrics gradually changed to yellowish-green and then yellow. Regardless of the natural dye, drastic overall color changes were observed, with average values of 7.60, 11.14, 12.68, and 13.56 Δ E CMC(2:1) at increasing rGO loadings of 1, 3, 5, and 7% owb, respectively.
Related collections
Most cited references37
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A roadmap for graphene.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Smart fabric sensors and e-textile technologies: a review
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found