- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Long noncoding RNA CASC9 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of papillary thyroid cancer via sponging miR‐488‐3p
Read this article at
Abstract
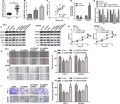
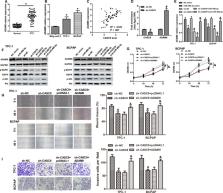
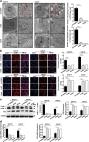
Cancer susceptibility candidate 9 (CASC9) is a recently identified lncRNA that acted as a tumor promotor in diversified cancer types. However, its role in papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) remains unknown. The expression of CASC9 was measured in 52 human PTC tissues and PTC cell lines as well as their controls. The proliferation, migration, and invasion of PTC cells were determined after knockdown or overexpression of CASC9 to evaluate the effect of CASC9 on PTC cells. Also, the role of PTC tumorigenesis was confirmed in mice xenograft models. Additionally, the underlying mechanisms of CASC9 were further researched. We found that CASC9 expression was augmented in human PTC tissues and cells. Higher CASC9 expression was associated with large tumor size, advanced stage, or lymph node metastasis. Downregulation of CASC9 significantly attenuated the proliferative, migrative, and invasive abilities of PTC cells, and suppressed tumorigenesis in vivo. While overexpression of CASC9 elevated the proliferation, migration, and invasion of PTC cells. miR‐488‐3p expression was decreased, and ADAM9 level was increased in PTC tissues and cells. CASC9 expression was negatively related to miR‐488‐3p, but positively associated with ADAM9 expression in PTC tissues. Molecular mechanism analysis revealed that CASC9 functioned via sponging miR‐488‐3p to regulate ADAM9 expression, followed by activation of EGFR‐Akt signaling. In conclusion, lncRNA CASC9 promoted the malignant phenotypes of PTC via modulating miR‐488‐3p/ADAM9 pathway. This study may provide a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of PTC.
Abstract
Related collections
Most cited references33
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Thyroid cancer
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Emerging roles of lncRNA in cancer and therapeutic opportunities.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found