- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Numerical Optimization Study of Combustion and Heat Transfer Characteristics in Municipal Solid Waste Incinerators
Read this article at
Abstract
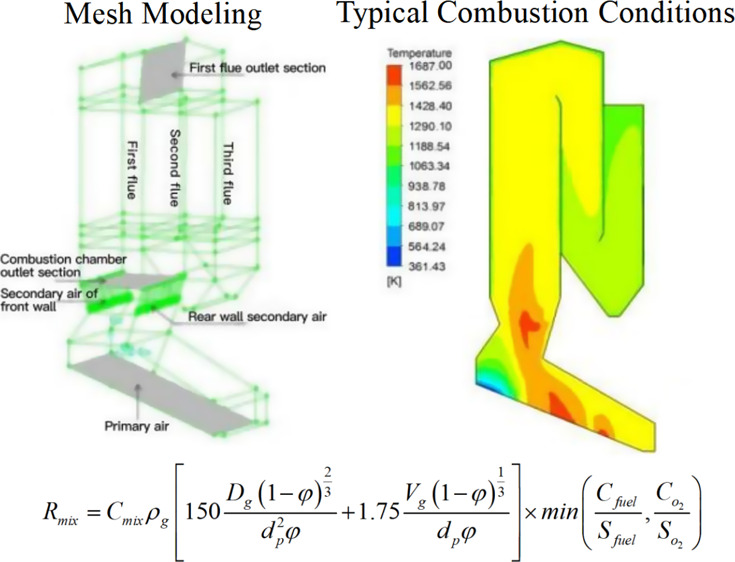
The efficient and clean utilization of urban waste can substitute for partial fossil fuels and reduce total carbon emissions. Fuel combustion is divided into three stages. Before the fire, the fuel is put into the furnace to reach the preparation stage of the fire temperature, the combustion stage takes place after the ignition temperature is reached, and finally, the combustion is completed. This article employs numerical simulation methods to comprehensively study the effects of various factors on the combustion characteristics of waste in a mechanical grate incinerator, including the inclination angle of the front arch, fuel properties, height of the front and rear arches, air distribution methods, and speed of the grate chain rotation. The results indicate that when the rear arch angle is set at 25°, the airflow distribution within the furnace is uniform and the high-temperature flue gas exhibits an ideal “L” shaped flow, achieving favorable characteristics of airflow distribution inside the furnace. With this structure, the airflow from the rear arch can adequately penetrate deep into the front arch area, thereby forming an efficient T-shaped combustion flame.
Related collections
Most cited references20
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of municipal solid wastes
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Pyrolysis characteristics of organic components of municipal solid waste at high heating rates
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found