- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Role of PGC-1α and Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Kidney Diseases
Read this article at
Abstract
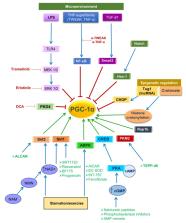
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is one of the fastest growing causes of death worldwide, emphasizing the need to develop novel therapeutic approaches. CKD predisposes to acute kidney injury (AKI) and AKI favors CKD progression. Mitochondrial derangements are common features of both AKI and CKD and mitochondria-targeting therapies are under study as nephroprotective agents. PGC-1α is a master regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis and an attractive therapeutic target. Low PGC-1α levels and decreased transcription of its gene targets have been observed in both preclinical AKI (nephrotoxic, endotoxemia, and ischemia-reperfusion) and in experimental and human CKD, most notably diabetic nephropathy. In mice, PGC-1α deficiency was associated with subclinical CKD and predisposition to AKI while PGC-1α overexpression in tubular cells protected from AKI of diverse causes. Several therapeutic strategies may increase kidney PGC-1α activity and have been successfully tested in animal models. These include AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activators, phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors, and anti-TWEAK antibodies. In conclusion, low PGC-1α activity appears to be a common feature of AKI and CKD and recent characterization of nephroprotective approaches that increase PGC-1α activity may pave the way for nephroprotective strategies potentially effective in both AKI and CKD.
Related collections
Most cited references154
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
KDIGO 2012 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mitochondrial energetics in the kidney
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found