- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Changing Climate and Pregnancy Health
Read this article at
Abstract
Purpose of Review
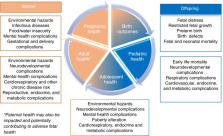
Climate change is the biggest public health threat of the twenty-first century but its impact on the perinatal period has only recently received attention. This review summarizes recent literature regarding the impacts of climate change and related environmental disasters on pregnancy health and provides recommendations to inform future adaptation and mitigation efforts.
Recent Findings
Accumulating evidence suggests that the changing climate affects pregnancy health directly via discrete environmental disasters (i.e., wildfire, extreme heat, hurricane, flood, and drought), and indirectly through changes in the natural and social environment. Although studies vary greatly in design, analytic methods, and assessment strategies, they generally converge to suggest that climate-related disasters are associated with increased risk of gestational complication, pregnancy loss, restricted fetal growth, low birthweight, preterm birth, and selected delivery/newborn complications. Window(s) of exposure with the highest sensitivity are not clear, but both acute and chronic exposures appear important. Furthermore, socioeconomically disadvantaged populations may be more vulnerable.
Summary
Policy, clinical, and research strategies for adaptation and mitigation should be continued, strengthened, and expanded with cross-disciplinary efforts. Top priorities should include (a) reinforcing and expanding policies to further reduce emission, (b) increasing awareness and education resources for healthcare providers and the public, (c) facilitating access to quality population-based data in low-resource areas, and (d) research efforts to better understand mechanisms of effects, identify susceptible populations and windows of exposure, explore interactive impacts of multiple exposures, and develop novel methods to better quantify pregnancy health impacts.
Related collections
Most cited references144
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The 2020 report of The Lancet Countdown on health and climate change: responding to converging crises
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Heat Stroke
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found