- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Early Deafened, Late Implanted Cochlear Implant Users Appreciate Music More Than and Identify Music as Well as Postlingual Users
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction: Typical cochlear implant (CI) users, namely postlingually deafened and implanted, report to not enjoy listening to music, and find it difficult to perceive music. Another group of CI users, the early-deafened (during language acquisition) and late-implanted (after a long period of auditory deprivation; EDLI), report a higher music appreciation, but is this related to a better music perception?
Materials and Methods: Sixteen EDLI and fifteen postlingually deafened (control group) CI users participated in the study. The inclusion criteria for EDLI were: severe or profound hearing loss onset before the age of 6 years, implantation after the age of 16 years, and CI experience more than 1 year. Subjectively, music perception and appreciation was evaluated using the Dutch Musical Background Questionnaire. Behaviorally, music perception was measured with melodic contour identification (MCI), using two instruments (piano and organ), each tested with and without a masking contour. Semitone distance between successive tones of the target varied from 1 to 3 semitones.
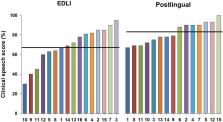
Results: Subjectively, the EDLI group reported to appreciate music more than postlingually deafened CI users. Behaviorally, while clinical phoneme recognition test score on average was lower in the EDLI group, melodic contour identification did not significantly differ between the two groups. There was, however, an effect of instrument and masker for both groups; the piano was the best-recognized instrument, and for both instruments, the masker with non-overlapping pitch was best recognized.
Discussion: EDLI group reported higher appreciation of music than postlingual control group, even though behaviorally measured music perception did not differ significantly between the two groups. Both surprising findings since EDLI CI users would be expected to have lower outcomes based on the early deafness onset, long duration of auditory deprivation, and on average lower clinical speech scores. Perhaps, the music perception difficulty comes from similar electric hearing limitations in both groups. The higher subjective appreciation in EDLI might be due to the lack of a musical memory, with no ability to compare music heard via the CI to acoustic music perception. Overall, our findings support a benefit from implantation for a positive music experience in EDLI CI users.
Related collections
Most cited references59
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Emotional responses to pleasant and unpleasant music correlate with activity in paralimbic brain regions.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Factors affecting auditory performance of postlinguistically deaf adults using cochlear implants: an update with 2251 patients.
