- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Physical activity practice and sports preferences in a group of Spanish schoolchildren depending on sex and parental care: a gender perspective
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Physical activity plays an important role in the maintenance of health, and it is especially important during childhood. However, the lack of information about differences in physical activity practice and sports preferences of children considering gender differences can result in non-effective policies that enhance inequalities between sexes. The aim of this study is to identify the sports preferences of Spanish schoolchildren and their physical activity practice behaviors depending on their sex and their parental care, analyzing the possible differences from a gender perspective.
Method
Three hundred sixty-four Spanish schoolchildren (179 girls, 185 boys) participated in this cross-sectional study. A daily physical activity questionnaire was used to evaluate physical activity level (PAL), moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) and sports preferences and a socio-health questionnaire were used to collect data about parental care. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS and applying Student’s T-test for normal variables, Mann-Whitney U-test for non-parametrical variables, and chi-square (χ2) test for categorical variables. Subsequently, odds ratios were used to analyze associations between the physical activity practice of the children and parental care.
Results
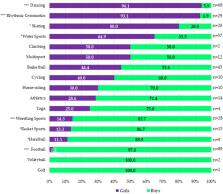
PAL and time spent in MVPA was significantly lower for girls compared to boys (1.44 ± 0.07 vs. 1.46 ± 0.07, p < 0.001 and 0.74 ± 0.40 h/day vs. 0.90 ± 0.45 h/day; p < 0.001, respectively). Dancing, rhythmic gymnastics, skating, and water sports were practiced more by girls, while football, wrestling sports, handball, and racket sports were practiced more by boys ( p < 0.05). Children cared for by their fathers had higher odds for physical activity practice (OR = 1.995 (1.202–3.310), p = 0.008).
Related collections
Most cited references44
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Canadian sedentary behaviour guidelines for children and youth.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Why Are Girls Less Physically Active than Boys? Findings from the LOOK Longitudinal Study

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found