- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
HSPA12B Secreted by Tumor-Associated Endothelial Cells Might Induce M2 Polarization of Macrophages via Activating PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling
Abstract
Purpose
The intratumoral microenvironment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSC) is highly immunosuppressive. In this study, we explored the potential functional role of HSPA12B secreted by tumor-associated endothelial cells (TECs) in M2 polarization of macrophages.
Materials and Methods
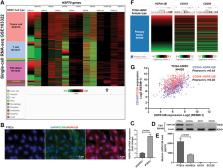
Bulk-seq data from TCGA-HNSC and single-cell RNA-seq data from GSE103322 (with over 5000 cells from 18 primary HNSC cases) were used for bioinformatic analysis. RAW264.7 cell line was used for in vitro studies.
Results
TECs in HNSC had significantly higher expression and secretion of HSPA12B, compared to normal human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Exogenous HSPA12B treatment increased the expression of M2 macrophage marker CD163 and CD206 on RAW264.7 cells in a dose-dependent manner but had no significant influence on CD86, an M1 macrophage marker. OLR1, a known receptor of HSP70 proteins, was specifically expressed in tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in HNSC. OLR1 knockdown significantly impaired HSPA12B uptake by RAW264.7 cells and weakened HSPA12B-induced CD163 and CD206 upregulation. HSPA12B treatment increased the expression of p-PI3K, p-Akt and p-mTOR in a dose-dependent manner in RAW264.7 cells. OLR1 inhibition and LY294002 treatment significantly weakened the effects HSPA12B on activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling and M2 marker expression.
Conclusion
Based on these findings, we speculated that aberrantly expressed and secreted HSPA12B by TECs could be taken by macrophages partly via OLR1, leading to subsequent activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and elevated expression of M2 markers. This mechanism shows a novel cross-talk between TECs and TAMs, which contributes to the intratumoral immunosuppressive microenvironment.
Most cited references26

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Macrophages in Tumor Microenvironments and the Progression of Tumors

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found