- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
miRNA-5119 regulates immune checkpoints in dendritic cells to enhance breast cancer immunotherapy
Meng Zhang ,
Yanmei Shi ,
Yujuan Zhang ,
Yifan Wang ,
Faizah Alotaibi ,
Li Qiu ,
Hongmei Wang ,
Shanshan Peng ,
Yanling Liu ,
Qing Li ,
Dian Gao ,
Zhigang Wang ,
Keng Yuan ,
Fang-fang Dou ,
James Koropatnick ,
Jianping Xiong ,
Weiping Min
February 20 2020
Read this article at
There is no author summary for this article yet. Authors can add summaries to their articles on ScienceOpen to make them more accessible to a non-specialist audience.
Related collections
Most cited references55
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Immune checkpoint blockade: a common denominator approach to cancer therapy.
Suzanne Topalian, Charles Drake, Drew M Pardoll (2015)
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
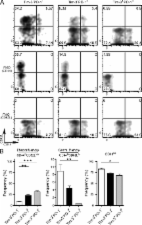
Targeting Tim-3 and PD-1 pathways to reverse T cell exhaustion and restore anti-tumor immunity
Kaori Sakuishi, Lionel Apetoh, Jenna Sullivan … (2010)
