- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Impact of comorbidity on waiting list and post-transplant outcomes in patients undergoing liver retransplantation
Read this article at
Abstract
AIM
To determine the impact of Charlson comorbidity index (CCI) on waiting list (WL) and post liver retransplantation (LRT) survival.
METHODS
Comparative study of all adult patients assessed for primary liver transplant (PLT) ( n = 1090) and patients assessed for LRT ( n = 150), 2000-2007 at our centre. Demographic, clinical and laboratory variables were recorded.
RESULTS
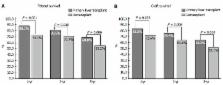
Median age for all patients was 53 years and 66% were men. Median model for end stage liver disease (MELD) score was 15. Median follow-up was 7-years. For retransplant patients, 84 (56%) had ≥ 1 comorbidity. The most common comorbidity was renal impairment in 66 (44.3%). WL mortality was higher in patients with ≥ 1 comorbidity (76% vs 53%, P = 0.044). CCI (OR = 2.688, 95%CI: 1.222-5.912, P = 0.014) was independently associated with WL mortality. Patients with MELD score ≥ 18 had inferior WL survival (Log-Rank 6.469, P = 0.011). On multivariate analysis, CCI (OR = 2.823, 95%CI: 1.563-5101, P = 0.001), MELD score ≥ 18 (OR 2.506, 95%CI: 1.044-6.018, P = 0.04), and requirement for organ support prior to LRT ( P < 0.05) were associated with reduced post-LRT survival. Donor/graft parameters were not associated with survival ( P = NS). Post-LRT mortality progressively increased according to the number of transplanted grafts (Log-Rank 18.455, P < 0.001). Post-LRT patient survival at 1-, 3- and 5-years were significantly inferior to those of PLT at 88% vs 73%, P < 0.001, 81% vs 71%, P = 0.018 and 69% vs 55%, P = 0.006, respectively.
Related collections
Most cited references37
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Acute renal failure in the ICU: risk factors and outcome evaluated by the SOFA score.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Liver transplantation in the United States, 1999-2008.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found