- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
eQTLs play critical roles in regulating gene expression and identifying key regulators in rice
Read this article at
Summary
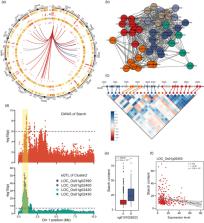
The regulation of gene expression plays an essential role in both the phenotype and adaptation of plants. Transcriptome sequencing enables simultaneous identification of exonic variants and quantification of gene expression. Here, we sequenced the leaf transcriptomes of 287 rice accessions from around the world and obtained a total of 177 853 high‐quality single nucleotide polymorphisms after filtering. Genome‐wide association study identified 44 354 expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs), which regulate the expression of 13 201 genes, as well as 17 local eQTL hotspots and 96 distant eQTL hotspots. Furthermore, a transcriptome‐wide association study screened 21 candidate genes for starch content in the flag leaves at the heading stage. HS002 was identified as a significant distant eQTL hotspot with five downstream genes enriched for diterpene antitoxin synthesis. Co‐expression analysis, eQTL analysis, and linkage mapping together demonstrated that bHLH026 acts as a key regulator to activate the expression of downstream genes. The transgenic assay revealed that bHLH026 is an important regulator of diterpenoid antitoxin synthesis and enhances the disease resistance of rice. These findings improve our knowledge of the regulatory mechanisms of gene expression variation and complex regulatory networks of the rice genome and will facilitate genetic improvement of cultivated rice varieties.
Related collections
Most cited references56
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found