- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
White sponge nevus of the oral cavity: Affecting members of two generations in a family
case-report
Read this article at
There is no author summary for this article yet. Authors can add summaries to their articles on ScienceOpen to make them more accessible to a non-specialist audience.
Abstract
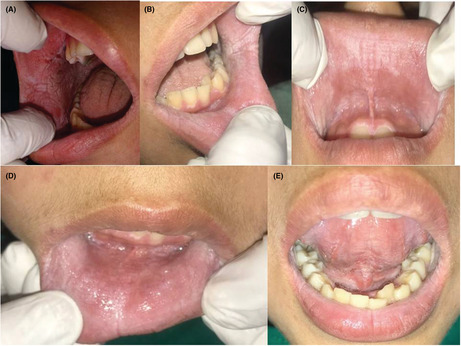
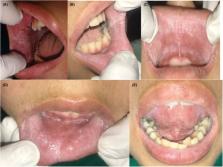
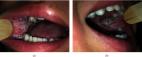
The typical feature is the autosomal dominant heritance and clinically dormant, non‐scarpalble, white diffuse, soft, thickened white plaques with a corrugated surface affecting mostly the buccal mucosa bilaterally which can substantially lead to the diagnosis of white sponge nevus.
Abstract
Related collections
Most cited references9
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A Case Report of Focal Epithelial Hyperplasia (Heck's disease) with PCR Detection of Human Papillomavirus.
Bora Ozden, Kaan Gunduz, Ömer Günhan … (2011)
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Constitutional mutation of keratin 13 gene in familial white sponge nevus.
Satoshi Yokoo, Jianming Zhang, Takahide Komori … (2003)
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Oral White Sponge Nevus: An Exceptional Differential Diagnosis in Childhood
Fatima Elfatoiki, Sophia Capatas, Hayat Dahbi Skali … (2020)