- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Pediatric sleep disturbances and treatment with melatonin
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
There are no guidelines concerning the best approach to improving sleep, but it has been shown that it can benefit the affected children and their entire families. The aim of this review is to analyse the efficacy and safety of melatonin in treating pediatric insomnia and sleep disturbances.
Main body
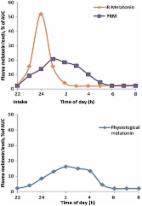
Sleep disturbances are highly prevalent in children and, without appropriate treatment, can become chronic and last for many years; however, distinguishing sleep disturbances from normal age-related changes can be a challenge for physicians and may delay treatment. Some published studies have shown that melatonin can be safe and effective not only in the case of primary sleep disorders, but also for sleep disorders associated with various neurological conditions. However, there is still uncertainty concerning dosing regimens and a lack of other data. The dose of melatonin should therefore be individualised on the basis of multiple factors, including the severity and type of sleep problem and the associated neurological pathology.
Conclusions
Melatonin can be safe and effective in treating both primary sleep disorders and the sleep disorders associated with various neurological conditions. However, there is a need for further studies aimed at identifying the sleep disordered infants and children who will benefit most from melatonin treatment, and determining appropriate doses based on the severity and type of disorder.
Related collections
Most cited references65
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
New perspectives on the role of melatonin in human sleep, circadian rhythms and their regulation
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The basic physiology and pathophysiology of melatonin.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found