- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Drug development in targeting ion channels for brain edema
Read this article at
Abstract
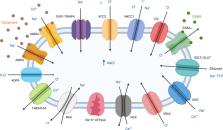
Cerebral edema is a pathological hallmark of various central nervous system (CNS) insults, including traumatic brain injury (TBI) and excitotoxic injury such as stroke. Due to the rigidity of the skull, edema-induced increase of intracranial fluid significantly complicates severe CNS injuries by raising intracranial pressure and compromising perfusion. Mortality due to cerebral edema is high. With mortality rates up to 80% in severe cases of stroke, it is the leading cause of death within the first week. Similarly, cerebral edema is devastating for patients of TBI, accounting for up to 50% mortality. Currently, the available treatments for cerebral edema include hypothermia, osmotherapy, and surgery. However, these treatments only address the symptoms and often elicit adverse side effects, potentially in part due to non-specificity. There is an urgent need to identify effective pharmacological treatments for cerebral edema. Currently, ion channels represent the third-largest target class for drug development, but their roles in cerebral edema remain ill-defined. The present review aims to provide an overview of the proposed roles of ion channels and transporters (including aquaporins, SUR1-TRPM4, chloride channels, glucose transporters, and proton-sensitive channels) in mediating cerebral edema in acute ischemic stroke and TBI. We also focus on the pharmacological inhibitors for each target and potential therapeutic strategies that may be further pursued for the treatment of cerebral edema.
Related collections
Most cited references272
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
TMEM16A confers receptor-activated calcium-dependent chloride conductance.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
TMEM16A, a membrane protein associated with calcium-dependent chloride channel activity.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
