- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the central nervous system: a focus on autoimmune disorders
Read this article at
Abstract
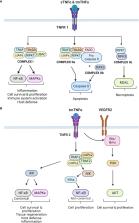
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) is a pleiotropic immune cytokine that belongs to the TNF superfamily of receptor ligands. The cytokine exists as either a transmembrane or a soluble molecule, and targets two distinct receptors, TNF-α receptor 1 (TNFR1) and TNF-α receptor 2 (TNFR2), which activate different signaling cascades and downstream genes. TNF-α cellular responses depend on its molecular form, targeted receptor, and concentration levels. TNF-α plays a multifaceted role in normal physiology that is highly relevant to human health and disease. In the central nervous system (CNS), this cytokine regulates homeostatic functions, such as neurogenesis, myelination, blood-brain barrier permeability and synaptic plasticity. However, it can also potentiate neuronal excitotoxicity and CNS inflammation. The pleiotropism of TNF-α and its various roles in the CNS, whether homeostatic or deleterious, only emphasizes the functional complexity of this cytokine. Anti-TNF-α therapy has demonstrated effectiveness in treating various autoimmune inflammatory diseases and has emerged as a significant treatment option for CNS autoimmune diseases. Nevertheless, it is crucial to recognize that the effects of this therapeutic target are diverse and complex. Contrary to initial expectations, anti-TNF-α therapy has been found to have detrimental effects in multiple sclerosis. This article focuses on describing the various roles, both physiological and pathological, of TNF-α in the CNS. Additionally, it discusses the specific disease processes that are dependent or regulated by TNF-α and the rationale of its use as a therapeutic target.
Related collections
Most cited references106
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Astrocytes: biology and pathology
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Multiple sclerosis
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found