- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mechanical Stress Induces Biotic and Abiotic Stress Responses via a Novel cis-Element
Read this article at
Abstract
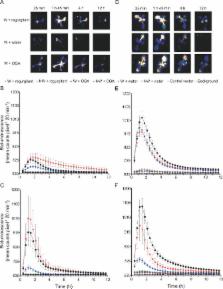
Plants are continuously exposed to a myriad of abiotic and biotic stresses. However, the molecular mechanisms by which these stress signals are perceived and transduced are poorly understood. To begin to identify primary stress signal transduction components, we have focused on genes that respond rapidly (within 5 min) to stress signals. Because it has been hypothesized that detection of physical stress is a mechanism common to mounting a response against a broad range of environmental stresses, we have utilized mechanical wounding as the stress stimulus and performed whole genome microarray analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana leaf tissue. This led to the identification of a number of rapid wound responsive (RWR) genes. Comparison of RWR genes with published abiotic and biotic stress microarray datasets demonstrates a large overlap across a wide range of environmental stresses. Interestingly, RWR genes also exhibit a striking level and pattern of circadian regulation, with induced and repressed genes displaying antiphasic rhythms. Using bioinformatic analysis, we identified a novel motif overrepresented in the promoters of RWR genes, herein designated as the Rapid Stress Response Element (RSRE). We demonstrate in transgenic plants that multimerized RSREs are sufficient to confer a rapid response to both biotic and abiotic stresses in vivo, thereby establishing the functional involvement of this motif in primary transcriptional stress responses. Collectively, our data provide evidence for a novel cis-element that is distributed across the promoters of an array of diverse stress-responsive genes, poised to respond immediately and coordinately to stress signals. This structure suggests that plants may have a transcriptional network resembling the general stress signaling pathway in yeast and that the RSRE element may provide the key to this coordinate regulation.
Author Summary
Plants are sessile organisms constantly challenged by a wide spectrum of biotic and abiotic stresses. These stresses cause considerable losses in crop yields worldwide, while the demand for food and energy is on the rise. Understanding the molecular mechanisms driving stress responses is crucial to devising targeted strategies to engineer stress-tolerant plants. To identify primary stress-responsive genes we examined the transcriptional profile of plants after mechanical wounding, which was used as a brief, inductive stimulus. Comparison of the ensemble of rapid wound response transcripts with published transcript profiles revealed a notable overlap with biotic and abiotic stress-responsive genes. Additional quantitative analyses of selected genes over a wounding time-course enabled classification into two groups: transient and stably expressed. Bioinformatic analysis of rapid wound response gene promoter sequences enabled us to identify a novel DNA motif, designated the Rapid Stress Response Element. This motif is sufficient to confer a rapid response to both biotic and abiotic stresses in vivo, thereby confirming the functional involvement of this motif in the primary transcriptional stress response. The genes we identified may represent initial components of the general stress-response network and may be useful in engineering multi-stress tolerant plants.
Related collections
Most cited references66
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Two transcription factors, DREB1 and DREB2, with an EREBP/AP2 DNA binding domain separate two cellular signal transduction pathways in drought- and low-temperature-responsive gene expression, respectively, in Arabidopsis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
