- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
USA300 Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus, United States, 2000–2013
Read this article at
Abstract
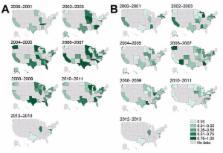
We confirm USA300 in the West and Midwest and subsequent diffusion to the East Coast.
Abstract
In the United States, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) with the USA300 pulsed-field gel electrophoresis type causes most community-associated MRSA infections and is an increasingly common cause of health care–associated MRSA infections. USA300 probably emerged during the early 1990s. To assess the spatiotemporal diffusion of USA300 MRSA and USA100 MRSA throughout the United States, we systematically reviewed 354 articles for data on 33,543 isolates, of which 8,092 were classified as USA300 and 2,595 as USA100. Using the biomedical literature as a proxy for USA300 prevalence among genotyped MRSA samples, we found that USA300 was isolated during 2000 in several states, including California, Texas, and midwestern states. The geographic mean center of USA300 MRSA then shifted eastward from 2000 to 2013. Analyzing genotyping studies enabled us to track the emergence of a new, successful MRSA type in space and time across the country.
Related collections
Most cited references26
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Waves of resistance: Staphylococcus aureus in the antibiotic era.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: epidemiology and clinical consequences of an emerging epidemic.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found