- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
High Efficient Visible-Light Photocatalytic Performance of Cu/ZnO/rGO Nanocomposite for Decomposing of Aqueous Ammonia and Treatment of Domestic Wastewater
Read this article at
Abstract
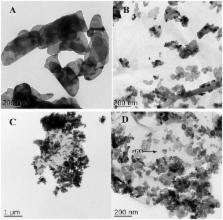
Photocatalytic removal of ammonium-nitrogen ( -N) from water using solar energy is an approach of high interest and applicability due to the convenience in application. ZnO has a great potential in photocatalytic decomposition of -N and conversion of this nutrient to under visible light irradiations. However the applicability of pristine ZnO though is limited due to its reduced capacity to utilize light from natural light. Herein, we report a two-step ZnO-modified strategy (Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles, immobilized on reduced graphene oxide (rGO) sheets) for the promotion of photocatalytic degradation of -N under visible light. UV-Vis spectra showed that the Cu/ZnO/rGO can be highly efficient in the utilization of photons from the visible region. Hence, Cu/ZnO/rGO managed to demonstrate adequate photocatalytic activity and effective -N removal from water under visible light compared to single ZnO. Specifically, up to 83.1% of -N (initial concentration 50 mg·L −1, catalyst dosage 2 g·L −1, pH 10) was removed within 2 h retention time under Xe lamp irradiation. From the catalysis, the major by-product was N 2. The high ammonia degradation efficiency from the ZnO/Cu/rGO is attributed to the improvement of the reactive oxygen species (ROSs) production efficiency and the further activation of the interfacial catalytic sites. This study also demonstrated that such nanocomposite is a recyclable agent. Its -N removal capacity remained effective even after five batch cycles. In addition, Cu/ZnO/rGO was applied to treat real domestic wastewater, and it was found that chemical oxygen demand (COD), total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) removal efficiencies can reach 84.3, 80.7, and 90.3%, respectively. Thus, Cu/ZnO/rGO in the presence of solar light can be a promising photocatalyst in the field of wastewater treatment.
Related collections
Most cited references44
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Ultrahigh electron mobility in suspended graphene
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Recent developments of zinc oxide based photocatalyst in water treatment technology: A review.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found