- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Regulation of indole‐3‐acetic acid biosynthesis and consequences of auxin production deficiency in Serratia plymuthica
Read this article at
Abstract
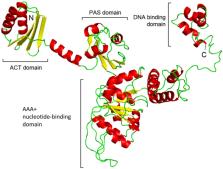
Indole‐3‐acetic acid (IAA) is emerging as a key intra‐ and inter‐kingdom signal molecule that modulates a wide range of processes of importance during plant–microorganism interaction. However, the mechanisms by which IAA carries out its functions in bacteria as well as the regulatory processes by which bacteria modulate auxin production are largely unknown. Here, we found that IAA synthesis deficiency results in important global transcriptional changes in the broad‐range antibiotic‐producing rhizobacterium Serratia plymuthica A153. Most pronounced transcriptional changes were observed in various gene clusters for aromatic acid metabolism, including auxin catabolism. To delve into the corresponding molecular mechanisms, different regulatory proteins were biochemically characterized. Among them, a TyrR orthologue was essential for IAA production through the activation of the ipdc gene encoding a key enzyme for IAA biosynthesis. We showed that TyrR specifically recognizes different aromatic amino acids which, in turn, alters the interactions of TyrR with the ipdc promoter. Screening of mutants defective in various transcriptional and post‐transcriptional regulators allowed the identification of additional regulators of IAA production, including PigP and quorum sensing‐related genes. Advancing our knowledge on the mechanisms that control the IAA biosynthesis in beneficial phytobacteria is of biotechnological interest for improving agricultural productivity and sustainable agricultural development.
Abstract
Related collections
Most cited references102
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Book: not found
