- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Efficacy of SGLT2 inhibitors as additional treatment in Japanese type 2 diabetic patients: second or third choice?
Read this article at
Abstract
Objectives
Due to the increase of type 2 diabetes (T2D), the number of patients in treatment with multiple anti-diabetic agents is increased. According to the recent recommendation of treatment guidelines, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors would be used as additional treatment to the currently administered anti-diabetic drugs for poorly controlled T2D patients. Here, we assessed the efficacy of SGLT2 inhibitors added to the current treatment with metformin, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibitors, or both in Japanese T2D patients.
Results
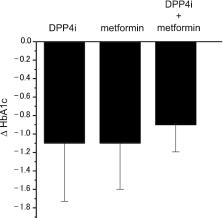
Japanese T2D subjects with poor glucose control, who were treated with metformin (n = 10), DPP4 inhibitors (n = 11), or both (n = 28) and who were in need of additional treatment, were recruited. HbA1c levels before and 6 months after addition of SGLT2 inhibitor treatment were used to compare the effectiveness. The HbA1c levels after addition of SGLT2 inhibitors significantly decreased in all groups. The change in HbA1c levels (delta HbA1c) showed no significant difference between the three groups. The present data indicated that addition of SGLT2 inhibitors to metformin and/or DPP4 inhibitors is equally effective in the treatment of Japanese T2D patients.
Related collections
Most cited references21
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2018. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD)
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Epidemic obesity and type 2 diabetes in Asia.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found