- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Streptococcus pneumoniae promotes migration and invasion of A549 cells in vitro by activating mTORC2/AKT through up-regulation of DDIT4 expression
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction
Dysbiosis of the lower airway flora is associated with lung cancer, of which the relationship between Streptococcus, especially pathogenic Streptococcus pneumoniae ( S. pneumoniae), and the progression of lung cancer are unclear.
Methods
Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) samples were prospectively collected from patients with pulmonary nodules during diagnostic bronchoscopy, and finally included 70 patients diagnosed with primary lung cancer and 20 patients with benign pulmonary nodules as the disease control group. The differential flora was screened by 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene amplicon sequencing. An in vitro infection model of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) cells exposed to S.pneumoniae was established to observe its effects on cell migration and invasion ability. Exploring the molecular mechanisms downstream of DDIT4 through its loss- and gain-of-function experiments.
Results
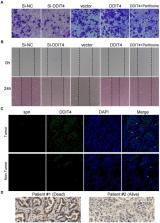
16S rRNA sequencing analysis showed that the abundance of Streptococcus in the lower airway flora of lung cancer patients was significantly increased. After exposure to S. pneumoniae, A549 and H1299 cells significantly enhanced their cell migration and invasion ability. The results of DDIT4 loss- and gain-of-function experiments in A549 cells suggest that up-regulation of DDIT4 activates the mTORC2/Akt signaling pathway, thereby enhancing the migration and invasion of A549 cells while not affecting mTORC1. Immunofluorescence (IF) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) showed that S. pneumoniae was enriched in LUAD tissues, and DDIT4 expression was significantly higher in cancer tissues than in non-cancerous tissues. The increased expression of DDIT4 was also related to the poor prognosis of patients with LUAD.
Discussion
The data provided by this study show that S. pneumoniae enriched in the lower airway of patients with lung cancer can up-regulate DDIT4 expression and subsequently activate the mTORC2/AKT signal pathway, thereby increasing the migration and invasion abilities of A549 cells. Our study provides a potential new mechanism for targeted therapy of LUAD.
Related collections
Most cited references41
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The human tumor microbiome is composed of tumor type–specific intracellular bacteria
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found