- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A nomogram for predicting 28-day mortality in elderly patients with acute kidney injury receiving continuous renal replacement therapy: a secondary analysis based on a retrospective cohort study
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common and serious condition, particularly among elderly patients. It is associated with high morbidity and mortality rates, further compounded by the need for continuous renal replacement therapy in severe cases. To improve clinical decision-making and patient management, there is a need for accurate prediction models that can identify patients at a high risk of mortality.
Methods
Data were extracted from the Dryad Digital Repository. Multivariate analysis was performed using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) logistic regression analysis to identify independent risk factors and construct a predictive nomogram for mortality within 28 days after continuous renal replacement therapy in elderly patients with acute kidney injury. The discrimination of the model was evaluated in the validation cohort using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), and calibration was evaluated using a calibration curve. The clinical utility of the model was assessed using decision curve analysis (DCA).
Results
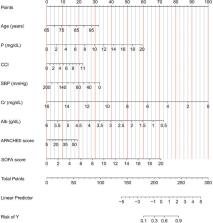
A total of 606 participants were enrolled and randomly divided into two groups: a training cohort ( n = 424) and a validation cohort ( n = 182) in a 7:3 proportion. A risk prediction model was developed to identify independent predictors of 28-day mortality in elderly patients with AKI. The predictors included age, systolic blood pressure, creatinine, albumin, phosphorus, age-adjusted Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II) score, and sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score. These predictors were incorporated into a logistic model and presented in a user-friendly nomogram. In the validation cohort, the model demonstrated good predictive performance with an AUC of 0.799. The calibration curve showed that the model was well calibrated. Additionally, DCA revealed significant net benefits of the nomogram for clinical application.
Related collections
Most cited references21
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Updating and validating the Charlson comorbidity index and score for risk adjustment in hospital discharge abstracts using data from 6 countries.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Acute Kidney Injury Network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found