- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Bevacizumab’s Association With a Decreased Risk of Brain Metastases in ECOG-ACRIN E1505, a Phase 3 Randomized Trial of Adjuvant Chemotherapy With or Without Bevacizumab in Surgically Resected NSCLC
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction
ECOG-ACRIN E1505 was a phase 3 randomized trial of adjuvant chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for patients with stages IB (>4 cm) to IIIA NSCLC. We sought to estimate the incidence and risk factors for brain recurrence as compared with extracranial recurrences (ECRs).
Methods
ECOG-ACRIN E1505 noted that bevacizumab failed to improve overall survival (OS) (OS hazard ratio [HR] = 0.99 [0·82–1·19], p = 0.90) or recurrence-free survival when added to chemotherapy in the adjuvant setting. The cumulative incidence of brain/ECR was estimated after adjusting for recurrence at other sites and death as competing events. A multivariable regression model was fitted using competing risk analysis to evaluate the effect of covariates on brain recurrence incidence.
Results
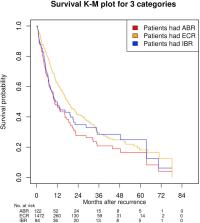
Median follow-up was 50.4 months. Among the 1501 patients enrolled, 472 developed ECR. There were 122 patients who had recurrence in the brain with or without simultaneous ECR as the first recurrence site (all-brain recurrences [ABRs]), and 84 of those with ABRs had recurrence in the brain only (isolated-brain recurrence [IBR]). The incidence of ABR, IBR, and ECR at 6 years was 9.9%, 5.9%, and 38.8%, respectively. Chemotherapy plus bevacizumab was associated with a decreased incidence of ABR (HR = 0.64, p = 0.02) and IBR (HR = 0.62, p = 0.032), but there was no significant trend for an OS decrement in the bevacizumab arm versus the control arm for both ABR and IBR. Median survivals associated with IBR, ABR, and ECR were 9.5, 9.5, and 14.1 months, respectively. Nonsquamous histology (HR = 1.87, p = 0.003) was also associated with ABR. ECR was associated with nonsquamous NSCLC histology (HR = 1.79, p < 0.01) and stage/N2 involvement (HR = 1.13/1.37, both p < 0.01).
Related collections
Most cited references41
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Atezolizumab for First-Line Treatment of Metastatic Nonsquamous NSCLC
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found