- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Cancer Stem Cells in Moderately Differentiated Buccal Mucosal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Express Components of the Renin–Angiotensin System
Read this article at
Abstract
Aim
We have recently identified and characterized cancer stem cell (CSC) subpopulations within moderately differentiated buccal mucosal squamous cell carcinoma (MDBMSCC). We hypothesized that these CSCs express components of the renin–angiotensin system (RAS).
Methods
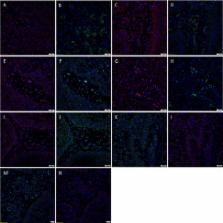
3,3′-Diaminobenzidine (DAB) immunohistochemical (IHC) staining was performed on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded MDBMSCC samples to investigate the expression of the components of the RAS: (pro)renin receptor (PRR), angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), angiotensin II receptor 1 (ATIIR1), and angiotensin II receptor 2 (ATIIR2). NanoString mRNA gene expression analysis and Western Blotting (WB) were performed on snap-frozen MDBMSCC samples to confirm gene expression and translation of these transcripts, respectively. Double immunofluorescent (IF) IHC staining of these components of the RAS with the embryonic stem cell markers OCT4 or SALL4 was performed to demonstrate their localization in relation to the CSC subpopulations within MDBMSCC.
Results
DAB IHC staining demonstrated expression of PRR, ACE, ATIIR1, and ATIIR2 in MDBMSCC. IF IHC staining showed that PRR was expressed by the CSC subpopulations within the tumor nests, the peri-tumoral stroma, and the endothelium of the microvessels within the peri-tumoral stroma. ATIIR1 and ATIIR2 were localized to the CSC subpopulations within the tumor nests and the peri-tumoral stroma, while ACE was localized to the endothelium of the microvessels within the peri-tumoral stroma. WB and NanoString analyses confirmed protein expression and transcription activation of PRR, ACE, and ATIIR1, but not of ATIIR2, respectively.
Related collections
Most cited references30
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Current concepts in management of oral cancer--surgery.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Aldehyde dehydrogenase activity selects for lung adenocarcinoma stem cells dependent on notch signaling.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found