- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Alterations of Lipid Metabolism in Cancer: Implications in Prognosis and Treatment
Read this article at
Abstract
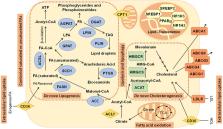
Cancer remains the second leading cause of mortality worldwide. In the course of this multistage and multifactorial disease, a set of alterations takes place, with genetic and environmental factors modulating tumorigenesis and disease progression. Metabolic alterations of tumors are well-recognized and are considered as one of the hallmarks of cancer. Cancer cells adapt their metabolic competences in order to efficiently supply their novel demands of energy to sustain cell proliferation and metastasis. At present, there is a growing interest in understanding the metabolic switch that occurs during tumorigenesis. Together with the Warburg effect and the increased glutaminolysis, lipid metabolism has emerged as essential for tumor development and progression. Indeed, several investigations have demonstrated the consequences of lipid metabolism alterations in cell migration, invasion, and angiogenesis, three basic steps occurring during metastasis. In addition, obesity and associated metabolic alterations have been shown to augment the risk of cancer and to worsen its prognosis. Consequently, an extensive collection of tumorigenic steps has been shown to be modulated by lipid metabolism, not only affecting the growth of primary tumors, but also mediating progression and metastasis. Besides, key enzymes involved in lipid-metabolic pathways have been associated with cancer survival and have been proposed as prognosis biomarkers of cancer. In this review, we will analyze the impact of obesity and related tumor microenviroment alterations as modifiable risk factors in cancer, focusing on the lipid alterations co-occurring during tumorigenesis. The value of precision technologies and its application to target lipid metabolism in cancer will also be discussed. The degree to which lipid alterations, together with current therapies and intake of specific dietary components, affect risk of cancer is now under investigation, and innovative therapeutic or preventive applications must be explored.
Related collections
Most cited references296
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cancer statistics, 2020
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found