- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Increased Prevalence of Anellovirus in Pediatric Patients with Fever
Read this article at
Abstract
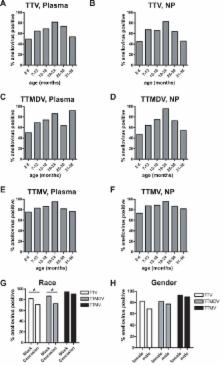
The Anelloviridae family consists of non-enveloped, circular, single-stranded DNA viruses. Three genera of anellovirus are known to infect humans, named TTV, TTMDV, and TTMV. Although anelloviruses were initially thought to cause non-A-G viral hepatitis, continued research has shown no definitive associations between anellovirus and human disease to date. Using high-throughput sequencing, we investigated the association between anelloviruses and fever in pediatric patients 2–36 months of age. We determined that although anelloviruses were present in a large number of specimens from both febrile and afebrile patients, they were more prevalent in the plasma and nasopharyngeal (NP) specimens of febrile patients compared to afebrile controls. Using PCR to detect each of the three species of anellovirus that infect humans, we found that anellovirus species TTV and TTMDV were more prevalent in the plasma and NP specimens of febrile patients compared to afebrile controls. This was not the case for species TTMV which was found in similar percentages of febrile and afebrile patient specimens. Analysis of patient age showed that the percentage of plasma and NP specimens containing anellovirus increased with age until patients were 19–24 months of age, after which the percentage of anellovirus positive patient specimens dropped. This trend was striking for TTV and TTMDV and very modest for TTMV in both plasma and NP specimens. Finally, as the temperature of febrile patients increased, so too did the frequency of TTV and TTMDV detection. Again, TTMV was equally present in both febrile and afebrile patient specimens. Taken together these data indicate that the human anellovirus species TTV and TTMDV are associated with fever in children, while the highly related human anellovirus TTMV has no association with fever.
Related collections
Most cited references50
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Rapid and quantitative detection of human adenovirus DNA by real-time PCR.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A novel DNA virus (TTV) associated with elevated transaminase levels in posttransfusion hepatitis of unknown etiology.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found